Root vegetables : complete list & guide
Root vegetables are edible underground plant parts, primarily roots, that store nutrients and energy for the plant. They are valued for their earthy flavors, dense textures, and high nutritional content. Common root vegetables include carrot, beetroot, radish, turnip, parsnip, rutabaga, celeriac, and daikon.
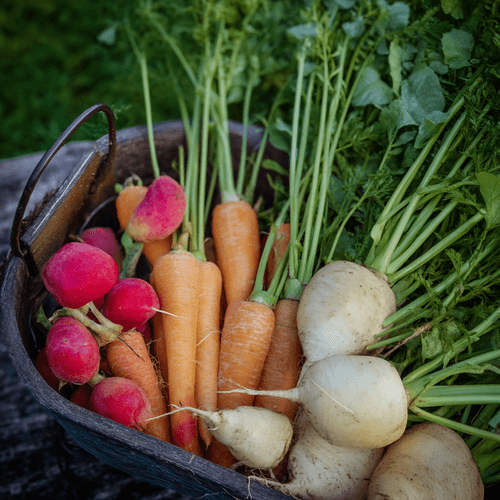
List of all root vegetables

Carrot

Radish
What to know about root vegetables ?
Master these fundamental concepts to become a successful gardener.
Name origin
Named for their edible root parts
Botanical classification
Various botanical families, including Apiaceae, Brassicaceae, Amaranthaceae, and others
Vegetable structure
Enlarged, fleshy taproots or storage roots that grow underground
Root vegetables in details
Root vegetables are a diverse group of edible plants cultivated mainly for their underground storage organs. They include carrots, beetroots, radishes, turnips, parsnips, rutabagas, celeriac, salsify, and daikon, among others.These vegetables are prized for their earthy, sweet, or peppery flavors and their dense, crisp, or tender textures. They are important sources of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamin C, potassium, folate, and a range of antioxidants and phytonutrients. Root vegetables are commonly eaten raw, roasted, boiled, mashed, or pickled, and are staples in many cuisines worldwide.Root vegetables grow best in loose, well-drained soils and are typically planted in spring or late summer. Most are annual or biennial plants that store energy in their roots to survive adverse conditions. Their ability to be stored for long periods makes them essential for food security, especially in colder climates and during winter months.In addition to their culinary uses, root vegetables have been valued in traditional medicine and are increasingly recognized for their health benefits and versatility in modern diets.
Related vegetable types

Leafy vegetables
