Did you know ?
- 1 Dried apricots have 3x more iron and fiber than fresh ones.
- 2 Armenia considers the apricot its national fruit.
- 3 Some apricot trees can live and produce fruit for over 100 years.
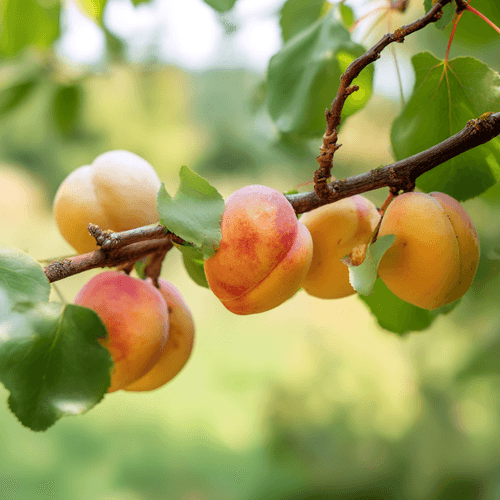
Apricots are small, golden-orange stone fruits with velvety skin and sweet-tart flesh. Rich in vitamins A and C, they are enjoyed fresh, dried, or in jams and desserts. Native to Central Asia, apricots thrive in temperate climates worldwide.
Did you know ?
View other Stone fruits
Nutrition
| Calories | 16 kcal |
| Proteins | 0.5g |
| Carbohydrates | 4g |
| of which sugars | 3g |
| Fiber | 0.7g |
| Fats | 0.1g |
Ripeness
Selection
Storage and ripening
If you bought unripe apricots, here's how to speed up the process :
Health
Origin
Apricots originated in Central Asia (China, Armenia, and Kazakhstan) over 4,000 years ago. They spread via the Silk Road to Europe and the Mediterranean. Today, Turkey, Iran, Italy, and Uzbekistan are leading producers.
Recipes
Gallery
There is no images yet. Submit one now to contribute to the gallery !
F.A.Q
Warnings
Larger, fuzzier, and juicier.
Firmer, darker, and more acidic.
Smooth-skinned, less tart.